Differences in their technologies andor factor endowments. Although the perfect factor mobility within each country international factor immobility.

Factor Endowment Definition Meaning In Stock Market With Example
They observed that comparative advantage arises from differences in national.

. It is a relatively poor predictor of real-world international trade patterns. The FPP will be concave and not linear as in the Ricardian case. Factor endowment theory is used to determine comparative advantage.
In economic reasoning the simplest case for this distribution is the idea that countries will have different ratios of capital to labor. Different factor intensities or combinations are required for the production of various goods. Differences in relative scarcity of factors of production in different countries resulting into different factor prices.
Specifically the more abundant a factor the lower its cost. Factor Endowment theory is known with different names such as Heckscher-Ohlin theory The Heckscher- Ohlin-Samuelson theory or the Factor Proportions theory. This paper studies the impact of factor endowment on international trade in a two-sector.
It argues that comparative advantage arises from differences in the countries labor productivity. The factor endowment theory holds that countries are likely to be abundant in different types of resources. Factor costs Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in factor costs.
While relation 4 suggests a means of estimating the quantitative importance of any given factor endowment difference it is based upon the. Factor Endowments Factor endowments refer to the extent to which a country is endowed with such resources as land labor and capital. Because we have two substitutable factors of production and not 1 with decreasing marginal productivity.
For example Panama exports bananas because it has a tropical climate the Congo exports copper because it has large deposits of this scarce ore. Cost advantages associated with large scale production. We compute non-parametric measures of technical efficiency for a sample of Moldovan small-holders using the four-step Data Envelopment Analysis DEA approach suggested by.
Vernons product life-cycle theory. We assume constant returns to scale and free trade. The difference in autarky relative prices between countries.
Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in factor costs. It lacks commonsense appeal. The Hecksher-Ohlin theory of factor endowment in international trade is used to determine comparative advantage of various countries.
Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in _____. This paper considers whether it is differences in technical efficiency or differences in factor endowments that explain productivity differentials in Moldovan agriculture. Who is the proponent of.
One key factor is geographic diversity that is differences in the climate and natural resources of different regions. Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in _____. 178 Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in _____.
The theory has been put forward by Swedish economists Eli Heckscher in 1919 and Bertin Ohlin in 1933. And different factor endowments explain differences in. Tries to isolate the impact of different factor endowments on the pattern of international trade.
Differences in factor intensity in the production of different goods. Simultaneously all sellers sell same goods. Kuwait exports oil because the country literally floats on a vast pool of it.
Assuming differences in both factor endowments and technologies to explain the pattern of international trade deviates from this spirit. The Heckscher-Ohlin theory predicts that countries will export those goods that make intensive use of factors that are locally abundant while importing goods that make intensive use of factors that. The Ricardian Classical model emphasized differences in technology.
Endowments were smaller the marginal products of the m resources would be less in India than in the United States if Indian resources of the m factors were increased to the United States level. When a country enjoys a relative abundance of a factor the factors relative cost is less than in countries where the factor is relatively scarce A countrys comparative advantage lies in the production of goods that. According to Ohlin the underlying forces behind differences in comparative costs are twofold.
The different goods require different factor-proportions for their production. Which of the following theories generates for government intervention and strategic trade policy. 1 Get Other questions on the subject.
The different regions or countries have different factor endowments. We start with the economy-wide revenue function. Differences in endowments of factors of production is the focus of the Heckscher-Ohlin model.
It does not explain the differences in national factor endowments. These differences determine comparative advantage. - 7929022 smirales8268 smirales8268 12252017 Biology High School answered expert verified.
A countrys endowment with resources such as land labor and capital. Jump to navigation Jump to search. Factor abundance versus factor scarcity.
The factor endowment are different between two countries. Nations have varying factor endowments and different factor endowments explain differences in factor costs. Efficiency of processes C.
Differences in factor endowments between countries. Y R Apv 1 Where Y is the value added A is the vector of total factor productivities p is the vector of. The theory states that the differences in the costs of production stems from the differences in the supply of factor endowments.
The goal of individual buy products is to maximize happines wheras the goals of firm sell products is to maximize profit. It cannot be subjected to many empirical tests. According to Ohlin trade between nations is based on the fact that there are differences in factor endowments.
Anything that produces different relative prices is a potential source of comparative advantage. Advantages accruing to the first to enter a market. The more abundant a factor the lower its cost.

Comparative Advantage And Factor Endowments Ppt Download
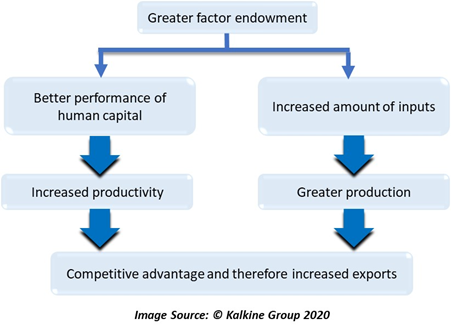
Factor Endowment Definition Meaning In Stock Market With Example

Factor Endowments And The Heckscher Ohlin Theory Economics Comparative Advantage Factors Of Production
0 Comments